Elevated CD4+ memory T-cells enable immune response to neoadjuvant atezolizumab in non-squamous NSCLC
Summary
This research focused on analyzing transcriptomic data from 180 non small-cell lung cancer patients treated with a PD-L1 blocking immunotherapy. We identified 214 genes associated with major pathologic response in patients with lung adenocarcinoma, including 85 genes indicative of immune cell presence. Immune deconvolution via TIMER2 and Spearman correlation analysis identified two immune cell subtypes associated with response: CD4+ memory-activated T cells and M1 macrophages. Future work will involve corroborating these results in the OAK and POPLAR lung cancer datasets, and investigating CD4+ and M1 macrophage expression in the single-cell data from this study.
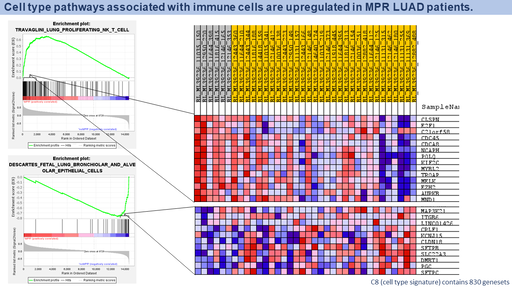
Figure. Geneset enrichment analysis revealed that LUNG_PROLIFERATING_NK_T_CELL genes were upregulated in patients who respond to immunotherapy.
